**1 Introduction**
Image information is one of the most intuitive forms of data in human perception, playing a crucial role in how we understand and interact with the world. With the rapid advancement of microelectronics technology, image information has evolved significantly—from analog to digital, from black and white to color, and from visible light to multi-spectral imaging. This evolution has led to substantial improvements in image quality, including resolution, clarity, and detail. However, as our demand for higher-quality images grows, challenges such as fog, low light, and poor visibility remain problematic, especially in visible light imaging, which closely mimics human vision. These issues often cannot be resolved through the imaging process alone and require post-processing. Additionally, in applications like image tracking, the time delay caused by image processing can severely limit the performance of servo systems. To address these challenges, this paper presents a real-time image dehazing enhancement system based on the TI TMS320C6455 DSP combined with an FPGA, and its application in practical engineering scenarios.
**2 System Structure and Working Principle**
**2.1 System Architecture**
The image dehazing enhancement system is built using a DSP+FPGA architecture. The DSP used is the TI TMS320C6455, a high-speed fixed-point digital signal processor developed on TI’s third-generation C6000 platform, operating at 1.2 GHz. It features 256 kbit of L1P program cache, 256 kbit of L1D data cache, 16 Mbit of L2 cache, a 64-bit EDMA controller, and an EMIF interface that supports 16-bit, 32-bit, and 64-bit data widths, with a maximum speed of 100 MHz. The FPGA is an Altera Stratix II series device, model EP2S60-F1020C5, featuring 60,440 logic units, 318,024 kbit of total RAM, 36 DSP blocks, 144 18x18 multipliers, 12 PLLs, and up to 718 I/O pins. For video encoding and decoding, the system uses the DS90CR285 and DS90CR286 chips.
**2.2 Working Principle of the System**
The system's structural block diagram is shown in Figure 1.








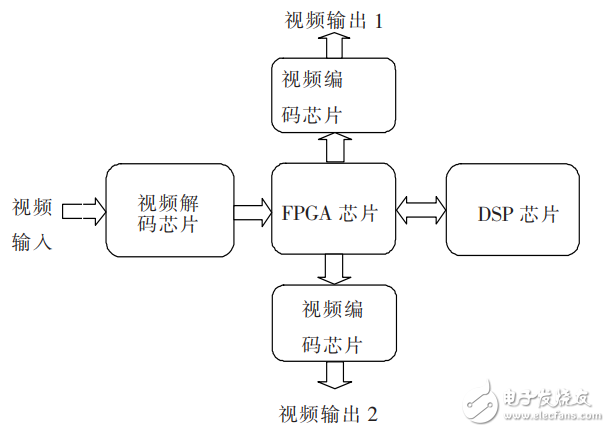
Figure 1: Real-time image dehazing enhancement system hardware block diagram
The DSP+FPGA architecture is a well-established, stable, and widely used hardware solution for image processing. In such systems, the FPGA typically acts as a scheduler, while the DSP handles the main image processing tasks. In applications like tracking, image data flows directly into the DSP, and processed results are output without significant delays. For real-time video processing, large volumes of image data can be input via EMIF, and output can be generated in real time. However, during dehazing and enhancement, the system must process and output images continuously, which requires buffering due to the limited bandwidth of the EMIF port. To avoid this delay, the proposed system offloads the dehazing algorithm to the FPGA, allowing the DSP to focus on parameter calculation. This approach eliminates the latency between the DSP and FPGA, and since the FPGA performs the task in hardware, the system achieves superior real-time performance.











lithium battery
zhejiang ttn electric co.,ltd , https://www.ttnpower.com