No oil, no charging, no exhaust gas — the only waste is pure water! Is there really such a car? The answer is yes! Toyota Mirai is one of them. But how does it work? Let’s dive into the technology behind this futuristic vehicle.

As fossil fuels continue to deplete, it's clear that traditional vehicles will eventually be replaced by new energy alternatives. While many are excited about electric cars, Toyota has long been at the forefront of innovation, especially with its hydrogen fuel cell technology. The Toyota Mirai is not just a concept; it's a real-world solution that represents the future of transportation.
Compared to electric vehicles, hydrogen fuel cells offer higher energy density and faster refueling times. Additionally, from an environmental standpoint, they have a greater impact in reducing carbon emissions than simply replacing gasoline with electricity. This makes hydrogen fuel cell technology a promising alternative for sustainable mobility.
The Mirai is a mass-produced hydrogen fuel cell vehicle, but what sets it apart from earlier hydrogen-powered cars? Unlike some models that directly use hydrogen to power the engine, the Mirai generates electricity through a fuel cell stack. This electricity then powers an electric motor, making it more efficient and similar to a battery electric vehicle in operation.

Understanding how the Mirai works is key. The process involves hydrogen reacting with oxygen in the fuel cell stack to generate electricity, which drives the motor. This seems simple, but the complexity lies in the system's design and efficiency.

Here's how it works: Hydrogen molecules split into protons and electrons at the anode. The protons pass through a membrane, while the electrons travel through an external circuit, creating electricity. At the cathode, the protons combine with oxygen and electrons to form water, which is the only byproduct. This entire process is clean and efficient.
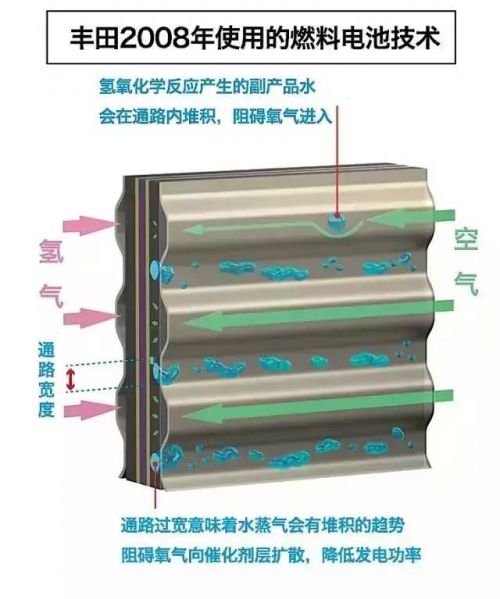
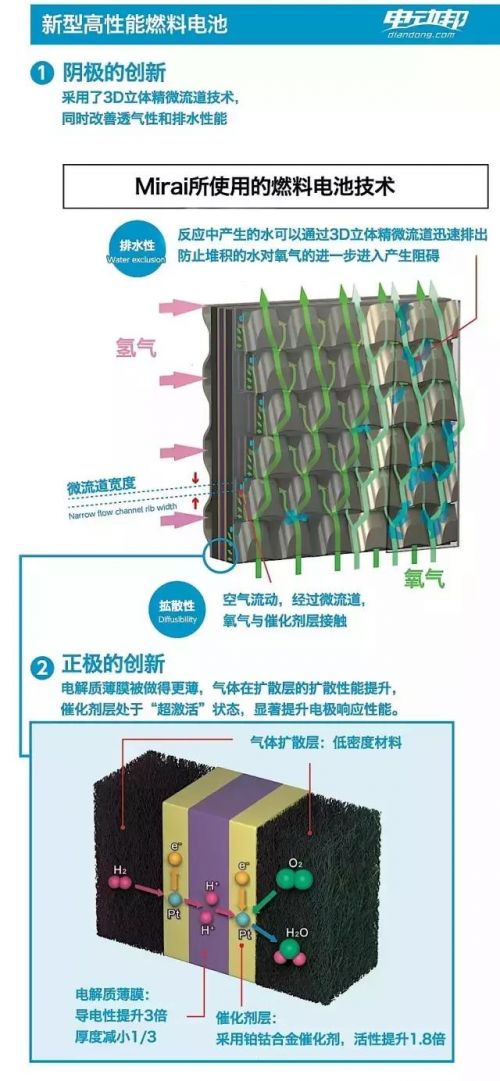
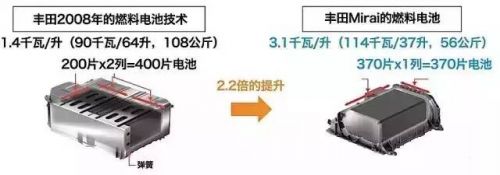
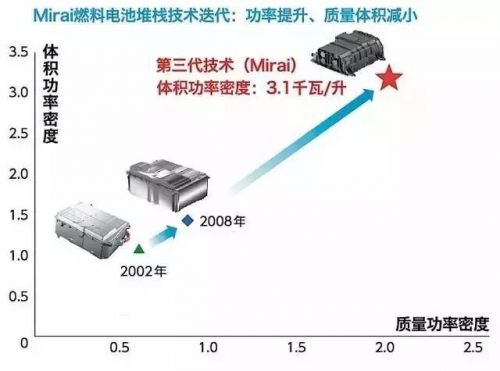
In 2008, Toyota introduced its first fuel cell prototype. Since then, the company has made significant improvements. The Mirai’s fuel cell stack consists of 370 thin-film cells, delivering 114 kW of power. Advanced technologies like 3D micro-channel design help improve efficiency and manage byproducts, making the system more compact and powerful.
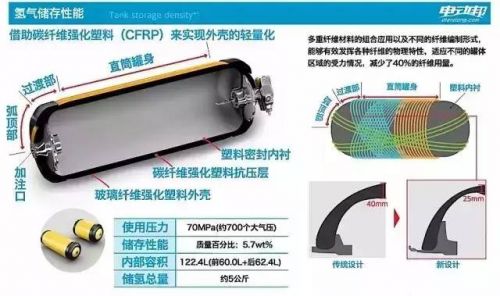
Safety is a top priority when it comes to hydrogen storage. The Mirai uses two high-pressure tanks capable of withstanding up to 70 MPa. These tanks are wrapped in protective layers, including carbon fiber Kevlar, ensuring they can withstand extreme conditions. This level of engineering gives drivers peace of mind.
The hydrogen storage system features a four-layer design. It starts with an aluminum alloy inner tank lined with plastic, then wrapped in carbon fiber reinforced plastic and a shock-absorbing glass fiber layer. Each layer is optimized for strength and safety, making the tank highly resistant to damage.
To power the motor, the fuel cell system boosts voltage from 250V to 650V using a boost converter. This ensures the Mirai can meet the power demands of its electric motor efficiently.
The Mirai’s motor delivers 113 kW of power and 335 N·m of torque, sourced from the Lexus RX450h. This powertrain is sufficient for the car’s weight and offers smooth performance suitable for daily driving.

One of the biggest advantages of hydrogen fuel cells over batteries is the quick refueling time, comparable to filling up a gasoline tank. Also, the range is significantly better than that of a battery-electric vehicle with a similar size battery pack.

Another unique feature of the Mirai is its ability to act as a mobile power source. With a power outlet on board, it can supply electricity to homes or devices during outages, turning the car into a “power treasure†in emergencies.

From a design perspective, the Mirai stands out with its modern, avant-garde look. Its slim headlights, dynamic lines, and distinctive taillights give it a futuristic appearance. Inside, the cabin blends familiar Toyota elements with fresh, innovative touches that reflect its advanced technology.

After the hydrogen is used, the only emission is water vapor, which is released through a dedicated pipe. This clean process highlights the environmental benefits of hydrogen fuel cell technology.

Despite its high-tech nature, the Mirai feels very approachable. Driving it is similar to a regular electric vehicle, making it easy for drivers to adapt without feeling overwhelmed by its advanced features.

Currently, the Mirai is available in Japan with a price around ¥380,000 (after taxes and fees, about ¥260,000). While it’s not cheaper than traditional mid-size cars, the cost of hydrogen fuel is expected to decrease in the future. The main challenge remains the limited number of hydrogen refueling stations.

In summary, the mass production of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles marks a significant step toward a sustainable future. While electric vehicles are popular, hydrogen fuel cells offer faster refueling and longer range, solving key limitations of battery EVs. The Toyota Mirai is not just a car—it's a glimpse into the future of transportation.







 HEE Series
HEE SeriesHeavy Duty Connector is a kind of connector, mainly used in industrial automation, equipment manufacturing and industrial system building and information and control technology and many other fields, also known as "industrial connector". The use of heavy-duty connectors not only helps manufacturers save installation time and reduce production costs, but also enables users to enjoy a more efficient and convenient use experience.
Hee Series Connector,Male Female Connector,High Density Industrial Connector,32 Pin High Density Connector
Kunshan SVL Electric Co.,Ltd , https://www.svlelectric.com