What is 5G?
 In the world of mobile communication, we’ve seen a remarkable evolution. The first generation (1G) was analog, used for basic voice calls. Then came 2G, which introduced digital voice and text messaging. The third generation (3G) brought us multimedia services and early mobile internet. 4G took it a step further, offering faster data speeds and paving the way for wireless broadband.
Now, 5G stands for the fifth generation of mobile communication technology. It's not just an upgrade—it's a transformation. While previous generations focused on improving speed and connectivity for people, 5G is designed to connect everything—people, devices, and even machines.
In the world of mobile communication, we’ve seen a remarkable evolution. The first generation (1G) was analog, used for basic voice calls. Then came 2G, which introduced digital voice and text messaging. The third generation (3G) brought us multimedia services and early mobile internet. 4G took it a step further, offering faster data speeds and paving the way for wireless broadband.
Now, 5G stands for the fifth generation of mobile communication technology. It's not just an upgrade—it's a transformation. While previous generations focused on improving speed and connectivity for people, 5G is designed to connect everything—people, devices, and even machines.
 So far, mobile technology has shifted from being "person-to-person" (3G) to "person-to-information" (4G). But 5G goes beyond that. It aims to create a truly intelligent, adaptable, and low-latency platform that supports future innovations. This means more than just faster downloads or smoother streaming—it’s about enabling new applications like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and industrial automation.
5G will support three key areas: enhanced mobile broadband, massive Internet of Things (IoT), and mission-critical communications. These areas extend far beyond smartphones and into industries such as healthcare, agriculture, transportation, and more. According to IHS Markit, 5G could impact over 21 industries, driving economic growth and business innovation.
So far, mobile technology has shifted from being "person-to-person" (3G) to "person-to-information" (4G). But 5G goes beyond that. It aims to create a truly intelligent, adaptable, and low-latency platform that supports future innovations. This means more than just faster downloads or smoother streaming—it’s about enabling new applications like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and industrial automation.
5G will support three key areas: enhanced mobile broadband, massive Internet of Things (IoT), and mission-critical communications. These areas extend far beyond smartphones and into industries such as healthcare, agriculture, transportation, and more. According to IHS Markit, 5G could impact over 21 industries, driving economic growth and business innovation.
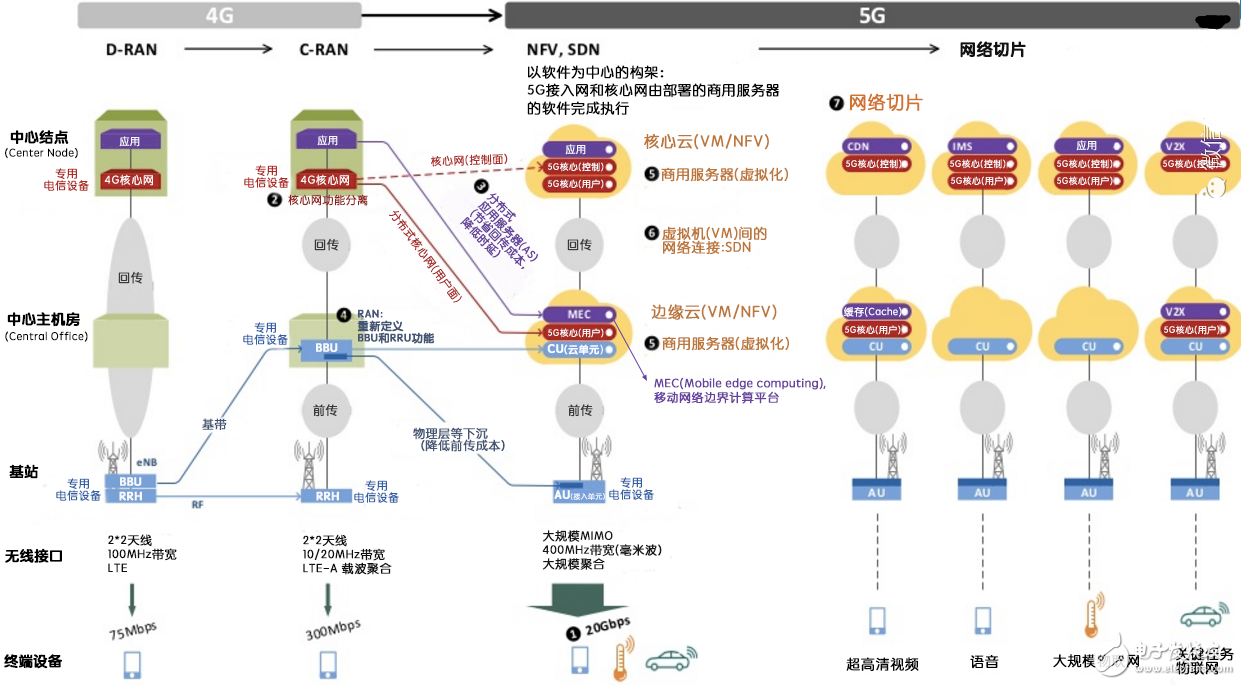 When comparing 5G and 4G, there are several key differences. First, 4G is already widely deployed, while 5G is still in the early stages of implementation, with large-scale rollout expected around 2020 and beyond.
Second, 4G networks primarily focus on providing bandwidth, whereas 5G is all about ubiquitous connectivity. It ensures reliable connections whether you're in a skyscraper or a subway station.
Third, 5G isn’t a standalone technology. It integrates with existing systems like 2G, 3G, LTE, Wi-Fi, and M2M (machine-to-machine) communication. This makes it ideal for supporting a wide range of applications, from IoT devices to augmented reality and immersive gaming.
Fourth, 5G can handle a huge number of connected devices and different types of traffic. For example, it can provide ultra-fast links for HD video streaming or low-speed connections for sensor networks.
Fifth, 5G uses new network architectures like cloud RAN and virtual RAN to create a more centralized and efficient system. It also leverages edge computing to process data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving performance.
Finally, 5G introduces cognitive radio technology, allowing the network to adapt dynamically. It can automatically choose the best frequency band, distinguish between mobile and fixed devices, and adjust itself in real time. This means 5G can support both industrial networks and consumer apps like social media.
In short, 5G isn’t just about speed—it’s about creating a smarter, more connected world.
When comparing 5G and 4G, there are several key differences. First, 4G is already widely deployed, while 5G is still in the early stages of implementation, with large-scale rollout expected around 2020 and beyond.
Second, 4G networks primarily focus on providing bandwidth, whereas 5G is all about ubiquitous connectivity. It ensures reliable connections whether you're in a skyscraper or a subway station.
Third, 5G isn’t a standalone technology. It integrates with existing systems like 2G, 3G, LTE, Wi-Fi, and M2M (machine-to-machine) communication. This makes it ideal for supporting a wide range of applications, from IoT devices to augmented reality and immersive gaming.
Fourth, 5G can handle a huge number of connected devices and different types of traffic. For example, it can provide ultra-fast links for HD video streaming or low-speed connections for sensor networks.
Fifth, 5G uses new network architectures like cloud RAN and virtual RAN to create a more centralized and efficient system. It also leverages edge computing to process data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving performance.
Finally, 5G introduces cognitive radio technology, allowing the network to adapt dynamically. It can automatically choose the best frequency band, distinguish between mobile and fixed devices, and adjust itself in real time. This means 5G can support both industrial networks and consumer apps like social media.
In short, 5G isn’t just about speed—it’s about creating a smarter, more connected world.



Door Contact Switch,Contact Switch For Door,Magnetic Door Contact Switch,Normally Open Door Contact
Shanghai Janetec Electric Co., Ltd. , https://www.janetecelectric.com