As we all know, high-definition video is relatively undoubtedly improved in terms of computer hardware requirements compared to standard-definition video such as rmvb and DVD.
This article refers to the address: http://
First, let's first take a look at what aspects of HD video have improved:
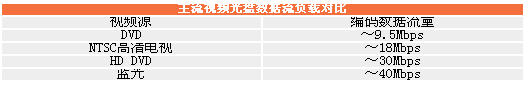
(1) The first is the increase in video traffic. This is the most intuitive upgrade element. We can refer to the following table. The table simply mentions the traffic comparison of “video sourceâ€, but the “different format†of HD video determines the difference of traffic.
It can be seen that the data traffic of DVD video is only about 9.5Mb/s, but the highest Blu-ray can reach more than 40Mb/s, which is more than 4 times. This is undoubtedly a major reason for the improvement of hardware configuration, because the amount of data to be processed It has increased a lot.
(b) The second is the complexity of the encoding format. We know that each encoding format has its own algorithm, and an excellent algorithm can compress the video to a smaller volume, but restoring this algorithm requires more computing power. The H.264 HD encoding format is a typical representative. Maybe some readers will encounter some high-definition video, but the playback requirements are not high. Maybe it is using some simple algorithms, such as Mpeg2's HD encoding format, but when it encounters similar H.264 encoding format, it will not play smoothly. Case.
It seems that H.264 has gained wide support because of its excellent algorithm. Although its algorithm is complex, it can get the highest compression and the video detail loss is very small. Therefore, it is necessary to smoothly play HD video in the future, H.264. Coded video is a test that must pass. Of course, we can't ignore VC-1 encoding. It is Microsoft's coding format and has been widely supported. Although its requirements are slightly lower, it also causes "playing difficulties" for many mainstream computers. As for Mpeg2 HD encoding, its requirements are very low, and the prospects for future development are not outstanding.
Let's take a look at how these codes are processed by the processor on the computer. The processing of video coding is generally divided into several steps, each step will complete the corresponding task, and these steps will also exist in the decoding, so as to achieve the smooth playback of the film. So who is going to handle these tasks? In the early days on the computer, most of the steps of decoding and playback were handled by the CPU, which is the decoding of the processor software (hereinafter referred to as soft solution). This is why the CPU usage is very high. the reason.
To put it simply, at present, any mainstream computer or even a few years ago, there is no problem with all standard-definition video before using the processor soft-release. In HD video, Mpeg2 HD encoding requires the lowest video, VC-1 encoded video is second, and the most demanding H.264 HD video may cause many old-fashioned computers to not play smoothly.
Although the hardware development speed is fast, users can use the high-end quad-core processor to control the CPU usage of the soft-release HD in less than 50%, but the price of such processors is very high, and the installed cost is greatly increased. The dual-core processor is a lot cheaper, but the CPU usage of the soft-decoding can be very high, even to the extent that it cannot be played smoothly.
If you want to reduce the burden on the CPU, you must have another accessory to take over the encoding process. The graphics card naturally becomes the best choice, that is, replacing the CPU with the engine in the graphics card to complete the video decoding processing task, thereby releasing the CPU load. The CPU is a general-purpose processor, and video decoding is limited in efficiency. However, the graphics card can directly integrate the video decoding engine into the hardware, thereby achieving extremely high efficiency.
Second, the encoding process of high-definition video
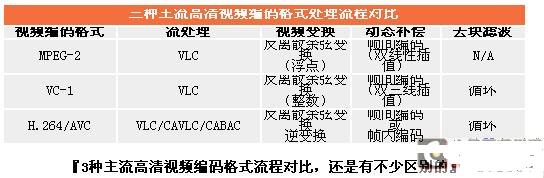
So what are the steps of HD encoding and which are the most loaded parts? In the case of H.264 video, it is divided into four main parts (see the figure below). The four blocks in the figure are basically the four main steps of H.264 decoding, and also the main four parts of resource consumption. Among them, the first step of "CAVLC/CABAC decoding" consumes the most computational resources, which is far higher. In the other three steps (simply, CAVLC/CABAC is two different algorithms in the H.264 coding specification, which increases the compression ratio, where CABAC has a higher compression ratio than CAVLC, but naturally requires higher decoding.) .
Third, the HD video decoding process
Let's take a look at the three mainstream encoding formats, including the decoding process of Mpeg2, VC-1, and H.264 (see the figure below). It can be seen that there are still many differences in several encoding formats, which is also the reason for the different encoding formats. The H.264 encoding format is the most complicated, so the system requirements are the highest, VC-1 is slightly reduced, but also better than Mpeg2 is much higher.

Other encoding formats are similar to H.264.
Fourth, HD decoding resource consumption analysis
So which step is the most CPU consumption? The following test comparison should best explain the problem (see the figure below). The comparison videos include Mpeg2 and H.264 (AVC), all of which are covered in the four steps above. Obviously, "streaming" is the most expensive part of all encoding formats, but this part of Mpeg2 video doesn't cause much trouble because the CPU usage is less than 2%.

However, for H.264, the problem arises. The video stream processing process with a 20Mb/s encoding rate will achieve a small CPU usage. The 40Mb/s high encoding rate video is more exaggerated. The process CPU of the stream processing. The occupancy rate rises extremely fast, and with other processing, it is not surprising that the total CPU usage is high.
As mentioned above, these four steps have different processing accessories, mainly CPU and graphics card. In the past, the CPU had a high occupancy rate because it processed more steps, so if the graphics card can take on more decoding steps, the CPU can release more load to ensure smooth video playback.
The decoding process of H.264 in the following figure is a good illustration of the problem. If the graphics card does not take any steps (the first line of the diagram), then the CPU usage is very high, and even can not be played smoothly; if the graphics card can achieve the decoding process of the last two steps (the second line of the diagram), the CPU can be partially liberated. However, for the more critical and most loaded "stream processing", some graphics cards can not be implemented, so the CPU usage has decreased, but it is still high.
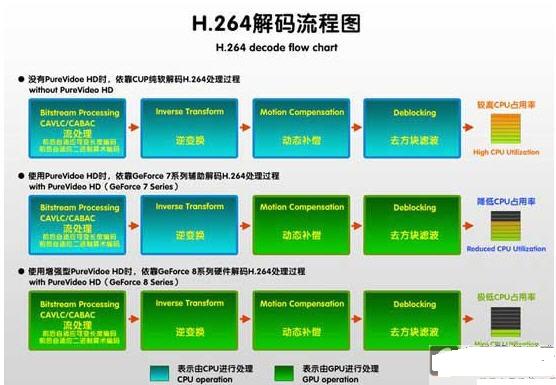
Through the graphics card with H.264 hardware decoding engine, you can complete all four processing steps of H.264 encoding (the third line of diagram), which is to achieve full decoding, which is the CPU that can make H.264 HD video playback. The root cause of the sharp decline in occupancy. Since the graphics card has completed all HD decoding processing, the CPU is naturally idle. The so-called partial decoding, that is, the CPU still undertakes certain processing tasks, so the occupancy rate is still much higher.
The Description Of Flat Amplified TV Antenna
Innovative flat,razor-thin antenna design.
Flat Amplified TV Antenna It has high gain and low error rate Digital TV signal reception,and a significant signal enhancement in actual ues.Increase the reception of TV programs,and eliminate the pause the mosaic images.
Multi-directional design pulls in signals from all directions.
Fast and easy to set up - Unwrap,Plug it in and Scan channels.
IMPORTANT TIP BEFORE YOU BUY:You have to make sure your TV is Digital TV, the local signal is COVERED.You can put it on the wall,on the table or on the window(strongly recommended) and it will make you enjoy watching crystal clear digital & HD shows with many opportunities.
The Specification Of Flat Amplified TV Antenna
Features
1.Support 1080p.
2.50 miles range.
3.Multi-directional capability.
4.call out all "Free" channels.
5.Connector Type:F Male.
6.V.S.W.R.:<1.5
7.Working Frequency: 174~240MHz,470~862MHz.
8.Gain:25 dBi(with amplifier).
Picture show


Flat Amplified TV Antenna,TV Antenna With Amplifier,Digital Flat TV Antenna,Flat TV Antenna
Shenzhen Yetnorson Technology Co., Ltd. , http://www.yetnorson.com