On August 18th, the Guihua Hall on the 6th floor of the Shenzhen Convention and Exhibition Center was hosted by the NB-IoT Industry Alliance. The China NB-IoT Industry Alliance Shenzhen Summit Forum hosted by the Internet of Things and the Shanghai Internet of Things Association was held lively. Recently, Huawei revealed in public that its NB-IoT commercial chip will take the lead in mass production in Q4 this year. The first national-level Internet of Things industry base will also land in Fuzhou, which indicates that China's NB-IoT industry will enter into substantive Force stage.
At the forum, more than 300 listeners were interested in NB-IoT's carrier deployment and technology hotspot issues. The Secretary-General of China NB-IoT Industry Alliance, Jie Yunzhou, gave wonderful answers to more than 20 major questions. The author shared the main points with the readers on the spot.

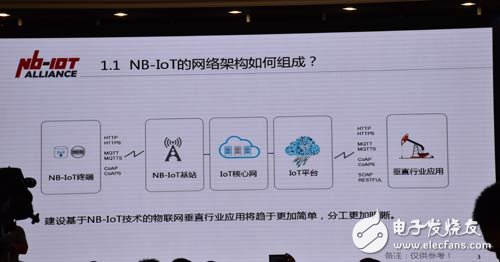
How is the network architecture of NB-IoT composed?
How are the frequency bands of NB-IoT allocated by operators at home and abroad?
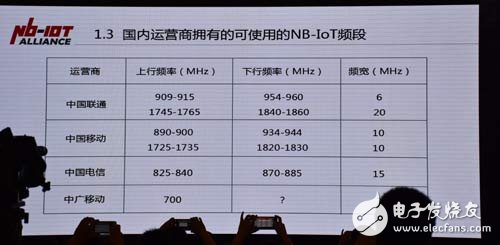
Most operators around the world use the 900MHz band to deploy NB-IoT, and some are deployed in the 800MHz band.
China Unicom's NB-IoT is deployed in the 900MHz and 1800MHz bands, and currently only 900 MHz can be tested. In order to build the NB-IoT Internet of Things, China Mobile will receive FOD photos and allow the re-cultivation of the 900MHz and 1800MHz bands.
China Telecom's NB-IoT is deployed in the 800 MHz band with a frequency of only 5 MHz.
What are the available NB-IoT bands owned by domestic operators?
NB-IoT network deployment schedule?
In 2016, China Unicom launched NB-IoT field-scale networking test based on 900MHz and 1800MHz frequency bands in seven cities (Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Fuzhou, Changsha, Yinchuan), and more than six business application demonstrations, 2018 The nationwide NB-IoT commercial deployment will begin.
China Mobile plans to launch the NB-IoT commercialization process in 2017. China Telecom plans to deploy the NB-IoT network in the first half of 2017.
Huawei has joined six operators (China Unicom, China Mobile, Vodafone, Emirates Telecom, Telefonica, etc.) to establish six NB-IoT open labs around the world, focusing on NB-IoT business innovation, industry development, interoperability testing and verification. . ZTE and China Mobile completed the technical verification demonstration of the NB-IoT protocol at the China Mobile 5G Joint Innovation Center Laboratory.
Does NB-IoT need a real name system?
Yes.
What is the operator's exit plan for 2G/3G networks?
China Unicom is likely to gradually shut down 2G networks in 2018, and in some places it may be to shut down 3G networks.
Japan's mobile carriers have all shut down 2G networks, AT&T in the US, Australia's Telstra and OPtus have announced plans to shut down the 2G network.
Telenor plans to close its 3G network in Norway by 2020, and then shut down its 2G network in 2025.
Some operators have considered the long-term existence of more than 100 million GPRS IoT terminals and low-end GSM mobile phones. Because of the low complexity of GSM and the lack of patent fees, the cost is lower than LTE for a long time. Most of them will maintain the GSM band to continue operations.
How can operators guarantee the stability of NB-IoT networks?
NB-IoT can be directly deployed on GSM, UMTS or LTE networks, and can be reused with existing network base stations to reduce deployment costs and achieve smooth upgrade. However, using a separate 180KHz band does not occupy the voice and data bandwidth of the existing network. The traditional business and the future IoT business section are stable and reliable at the same time.
The control and bearer separation of the NB-IoT, the signaling control plane, and the data bearer plane, if it is a low-rate service, the control is directly performed, and the dedicated bearer is no longer established, and the signaling process of the NAS and the core network is omitted. Wake up recovery delay.
NB-IoT is a serviceable telecommunication network, which is the key to distinguishing NB-IoT from LoRa and SigFox technologies.
How do operators profit from NB-IoT networks?
The QoS service quality assurance, network security, carrier-class billing, and big data services continue to maintain industry advantages. The NB-IoT network enables operators to enhance the service capabilities of the Internet of Things, including cloud service provision. Massive customer management, real-time authentication of the Internet of Things, system integration, high-end customized services for large customers.
The price issue associated with NB-IoT?
Operator tariff: one is based on traffic billing, one is billed by message, and the trend will be lower than GPRS fee.
Chip price: lower than 2G main chip, reasonable expectation price of 1 US dollar.
Module price: lower than the GPRS module price, reasonable expectation price of 2 US dollars.
Terminal price: Pricing based on actual function.
Maintenance costs: much lower than existing network maintenance costs
Subsidy policy: The early operators will provide greater operating subsidies.
Mineral Insulated Cable,Copper Mineral Insulation Cable,Copper Core Copper Sheath Cable,Fire Resistant Cable
Baosheng Science&Technology Innovation Co.,Ltd , https://www.bscables.com